CCTV
All CCTV systems are not created equally. The right CCTV system for you is dependent on what you want the system to be cable of.

Selecting the correct equipment
Closed Circuit Television (CCTV) is the use of video cameras in a closed circuit to remotely view a particular location and then transmit a signal to a specified place, usually a monitor or recording device. CCTV has become integrated into the security programs of many businesses and represents a significant aid to police in investigating crime and providing evidence which may lead to the prosecution of offenders.
CCTV Images
When developing the objectives of a CCTV system, consideration should be given to whether the system is designed to identify, recognise, detect or observe.
-

Identify – The picture quality and detail should be sufficient to enable the identity of a subject to be established beyond reasonable doubt or a vehicle licence plate to be read without enhancement. The subject target occupies 120 per cent of the height of the screen image when using standard definition cameras -

Recognise – The subject target should occupy 50 per cent of the screen image height with sufficient detail to identify a known person or establish colour, make and model of a vehicle. -

Detect – Subject target occupies 10 per cent of the screen image height with sufficient detail to detect activity within the camera’s field of view, establish the activities or circumstances of an event such as the movements and activities of persons or vehicles. -

Observe – Target subject occupies five per cent of the screen image height and enables movements to be observed including tracking, or the number of persons involved and other
activities.
When considering installing CCTV the risk management process plays an important role. Risk management assists to identify threats to your organisation’s assets including people, property and information, and determine vulnerabilities or weaknesses in your organisation’s security program which may reveal CCTV to be a cost effective treatment to support your security functions. Before introducing CCTV into any organisation it is essential to establish aims and objectives, or specifically, what is it that you expect to achieve from the installation of CCTV. CCTV may deter and/or detect crime, provide evidence to the police in the event of a crime as well as promote the perception of safety and reduce the fear of crime among your clients, staff and the general public.
What Does my CCTV System Need to Do?
CCTV systems may be used to investigate crime and prosecute offenders. Police specifically require the ability to identify offenders and/ or vehicles, therefore a great deal of thought should be undertaken prior to investing in CCTV. Inexpensive systems, while abundant and easy to install, may prove to be unsuccessful when a crime has occurred and police proceed to investigate only to find that the images have been overwritten or are of poor quality. A good CCTV system is one that achieves its operational objectives and may represent a substantial capital investment. Consequently, consideration should be paid to its design, capability and the quality of the images it delivers. Images from CCTV systems should be good enough to achieve its objectives without enhancement, e.g. digital zoom in.
CCTV Recording Systems
There are a number of systems used to record CCTV images. Digital technology has paved the way for CCTV video images to be recorded to large capacity hard drives similar to those used in PCs. There are Digital Video Recorders (DVRs) and Network Video Recorders (NVR) which record images from cameras directly connected to the recorders. However, IP (Internet Protocol) cameras or centralised IP cameras used with an NVR do not need supporting infrastructure such as power at the site of the camera. Instead, IP cameras use power over Ethernet (PoE) whereby power and data can be passed over the same cable usually Cat 5 or Cat 6. Should you wish to incorporate your existing analogue cameras with new IP cameras, hybrid recording systems are available that are capable of recording both.
Physical Location NVR
CCTV recorders should be secured from unauthorised access. Recording units must have protection from interference with its recording, archiving and system operation. Access to live images should also be restricted to those persons who need to view live camera images. Most systems are equipped with password protection or key locks to prevent unauthorised access. As CCTV systems are mostly electronic components they should be free from exposure to dust, extreme temperatures, humidity and other airborne and environmental conditions.
Archive Capacity
It is recommended that archive capacity is calculated to achieve 31 days or more of available images before overwrite occurs as per Australian Standard AS 4806.1.
Archive capacity should be increased as an alternative to reducing frame rates or image resolution quality. A feature of modern CCTV systems is a function known as movement detection where the recording system only records when movement is detected within the camera’s field of view. This not only saves archive space but assists when reviewing vision because there is less vision to search.
Battery Back-up
In order that the security function of a location continues during localised or widespread power interruptions, cameras and recording devices should be connected to the essential services power supply of a building or a designated UPS (uninterrupted power supply). This minimises the risk of overriding the security protection system of your establishment from interference with the power supply.
Analogue / HD-TVI or IP Cameras?
Cameras have varying degrees of quality, resolution and capability and some have the ability to view scenes in low light conditions. A camera’s clarity can be measured in TV lines or pixels. Analogue cameras are measured in TV lines and IP network cameras are measured in pixels. The higher number of TV lines or pixels the more superior the detail achieved.
What Type of Camera?
There are two types of camera configurations. These are known as ‘fixed’ cameras whereby the camera is mounted in a stationary position and view the same scene until physically relocated and ‘PTZ’ (pan, tilt, zoom) cameras which are motor driven with remote control over the observation direction, focus and zoom capabilities of a camera.
Camera Placement
By developing your objectives and using the risk management process it will become clear as to what assets are in need of protection and the best possible location of CCTV cameras. Each camera should fulfil its objectives to identify, recognise, detect or observe persons, vehicles or other activities regardless of the time of day and environmental conditions. Cameras may need protection from vandalism or interference however this does not necessarily mean that cameras should be placed in an elevated position away from a vandal’s reach. It is more important to maintain the camera’s original objective therefore physical protection of the camera may be necessary by introducing protective enclosures. The risk of camera theft can be minimised by the addition of tamper switches connected to an alarm system which will trigger sirens, strobe lights and communicate the interference to the alarm system’s monitoring centre for appropriate action.
Which Camera lens
CCTV cameras require the correct lens to achieve their full potential. Lens size and type is as crucial to the effective use of CCTV as the camera or any other component of the system. Lens size requires calculations to achieve the desired image. As a basic guide, lens size is calculated from the height of the image sensor (charge-coupled device or CCD) used to convert light into digital images. CCDs range in size from 1/6 inch to 1 inch. The larger the CCD the more light it can capture and the better the images. The height of the CCD forms part of these calculations as detailed below:
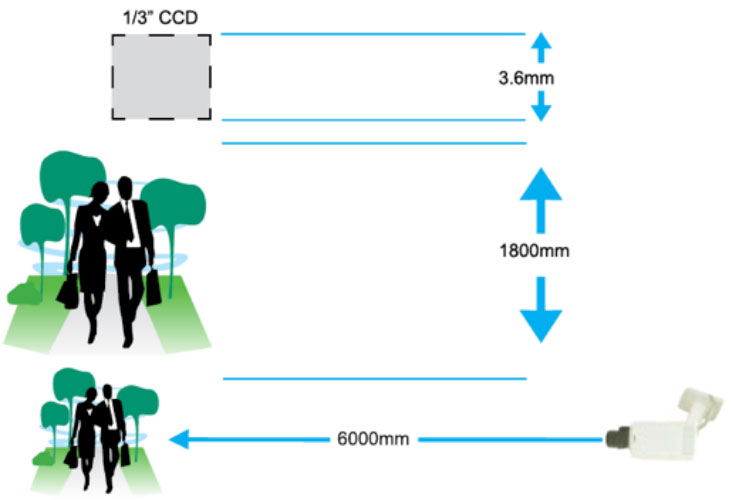
1/3” CCD has a height of 3.6mm, divided by height of subject target of 1800mm and multiplied by distance from the camera at 6000mm.
3.6 mm x 6000mm = 12mm lens
1800mm
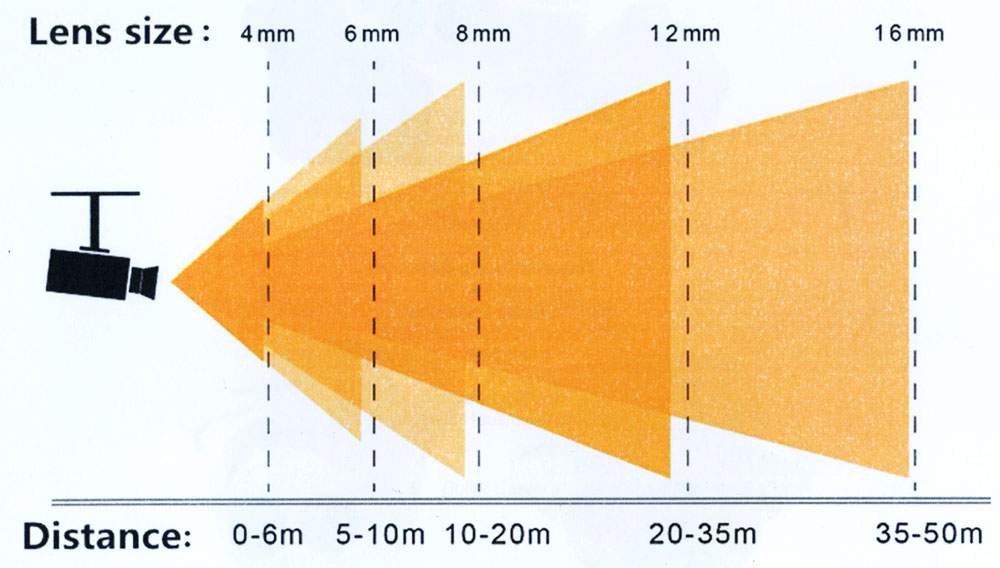
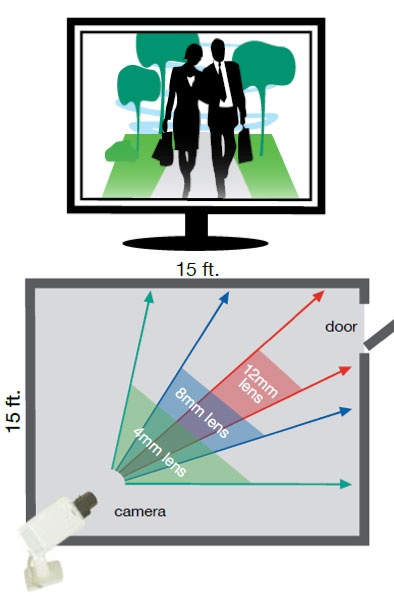
Field of View
The Field of View (FOV) is based on the camera and the lens. By increasing the size of the lens or the focal length, a decrease in the FOV occurs. The perceived view of the object, or how far the object is seen on the screen is improved with higher numbered lenses but narrows the FOV.
How do I provide CCTV Footage to Police?
Recorded vision can be exported to portable media such as CD/DVD, USB or flash drives.
Maintenance of CCTV equipment
Regular maintenance of CCTV systems is possibly the area that is most neglected. CCTV systems require maintenance of camera lenses (focus and alignment), cleaning of enclosures and viewports, adjustment
of recorders’ time and date to allow for daylight saving, and correct operation of the recording units, and uninterrupted power supplies.
Other Considerations
When installing CCTV cameras there are a number of other factors that need consideration including:
- Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED).
- Correct lighting to illuminate the target area without causing glare. This includes glare from windows or reflected glare from floor surfaces, buildings or vehicle headlights in the field of view of the camera.
- The camera’s performance at night under low light or artificial lighting conditions.
- Vegetation, including its potential growth and movement in windy conditions.
- The effects of the sun, taking into account its seasonal positions.
- Objects that are subject to movement including banners, posters or suspended objects that may trigger the activity detection function of the CCTV system causing valuable archive space to be consumed.
- Environmental conditions (wet/dry/dusty/coastal/hot/cold/day/night).
- CCTV Signage
The location of CCTV signage should also be considered. Australian Standard AS4806.1 – 2006 Closed Circuit Television – Management and Operation states that (as a minimum) CCTV signage be posted at all CCTV system site entries. Signage placed at face level may be more easily noticed, however signage mounted higher may assist in preventing vandalism, theft or graffiti. Signage should be provided adequate illumination, be visible and legible at all times.
Taking advantage of modern technology

Advances in digital technology have meant that images from your CCTV system are now accessible from any device, any where in the world, allowing you to “check-up” on your business or property from the other side of the world. Some camera systems are sophisticated enough to allow the operator to remotely move the camera.
CommsCentre are experts at selecting and installing the correct CCTV system for your business or home. Contact us today to find out more.
Showing all 12 results
-

Hikvision 1.3MP Outdoor Dome, IP66, 3D DNR, EXIR IR Tech, 4mm Fixed Lens
Read more -

Hikvision 3MP Bullet Camera, 3D DNR, EXIR IR Tech, 4mm Fixed Lens
Read more -

Hikvision 3MP Bullet Camera, 3D DNR, IR, 4mm Fixed Lens
Read more -

Hikvision 3MP Bullet Camera, IP66, D/N, 3D DNR, DWDR, BLC, IR, 2.8-12mm
Read more -
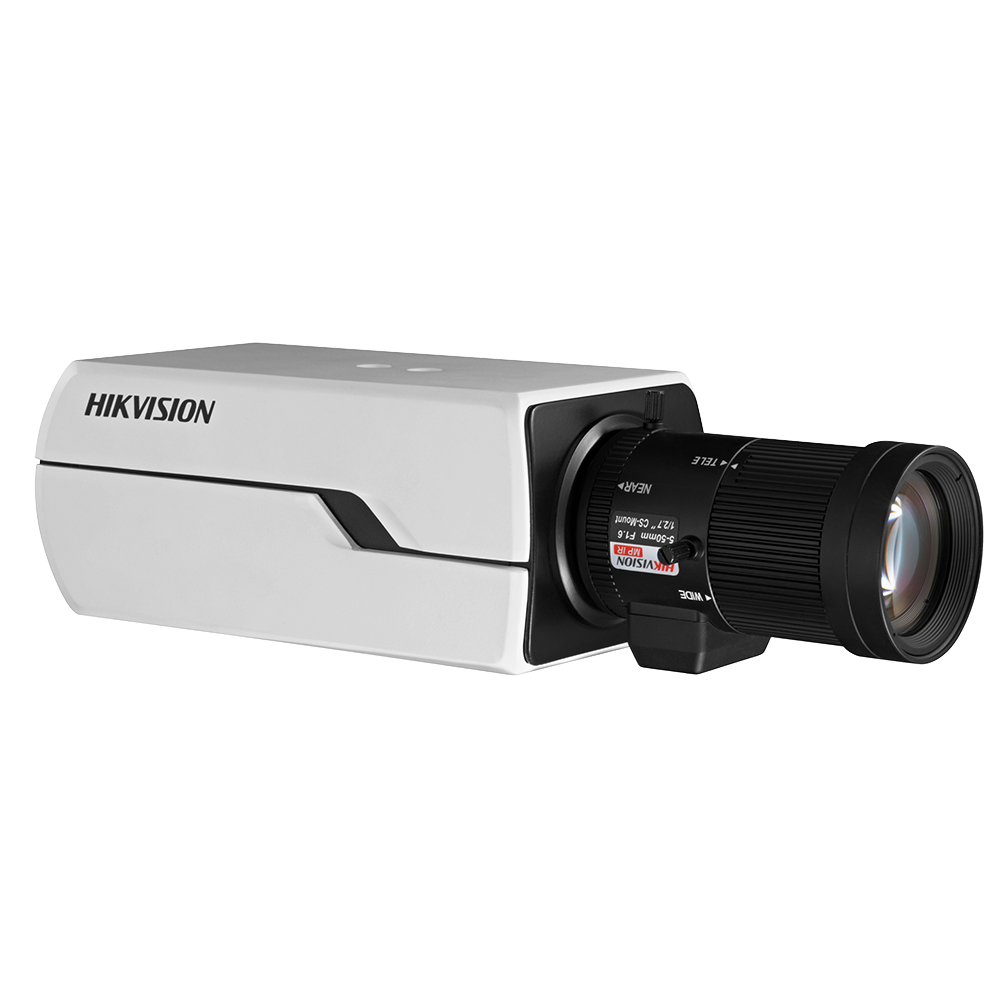

Hikvision 3MP Full Body Camera, WDR, 3DNR, Defog, ABF (Lens not included)
Read more -
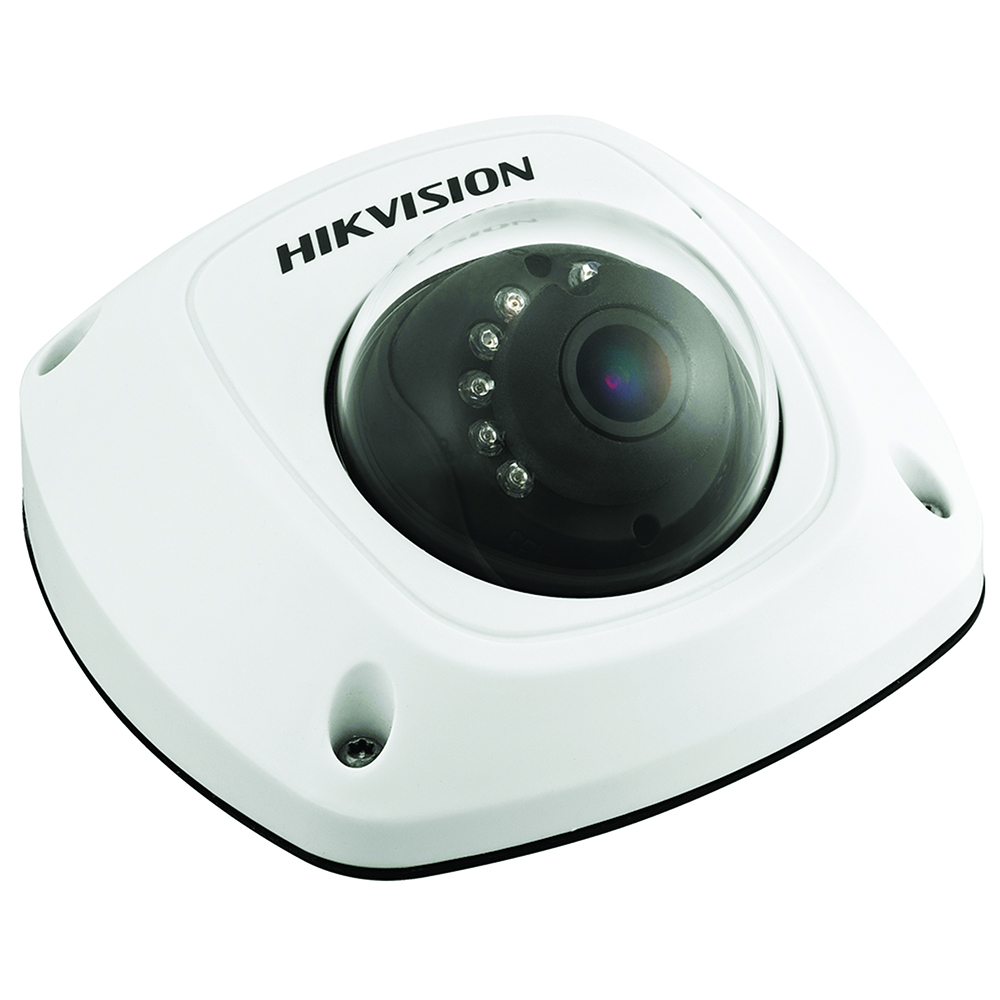

Hikvision 3MP IR Mini Dome, Full HD, 3D DNR, DWDR, PoE, 2.8mm Fixed Lens, IP66
Read more -
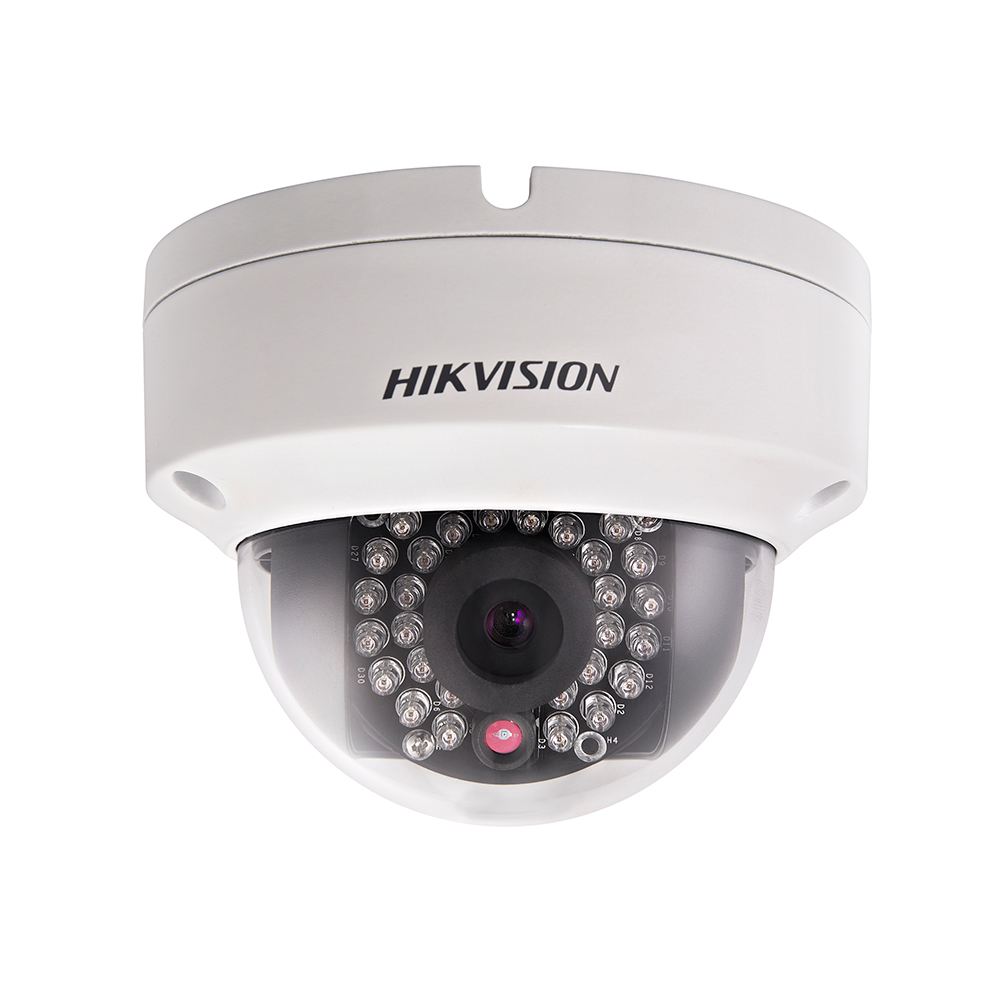

Hikvision 3MP Outdoor Dome, IP66, DN, 3D DNR, DWDR, BLC ,IR, 4mm Fixed Lens
Read more -
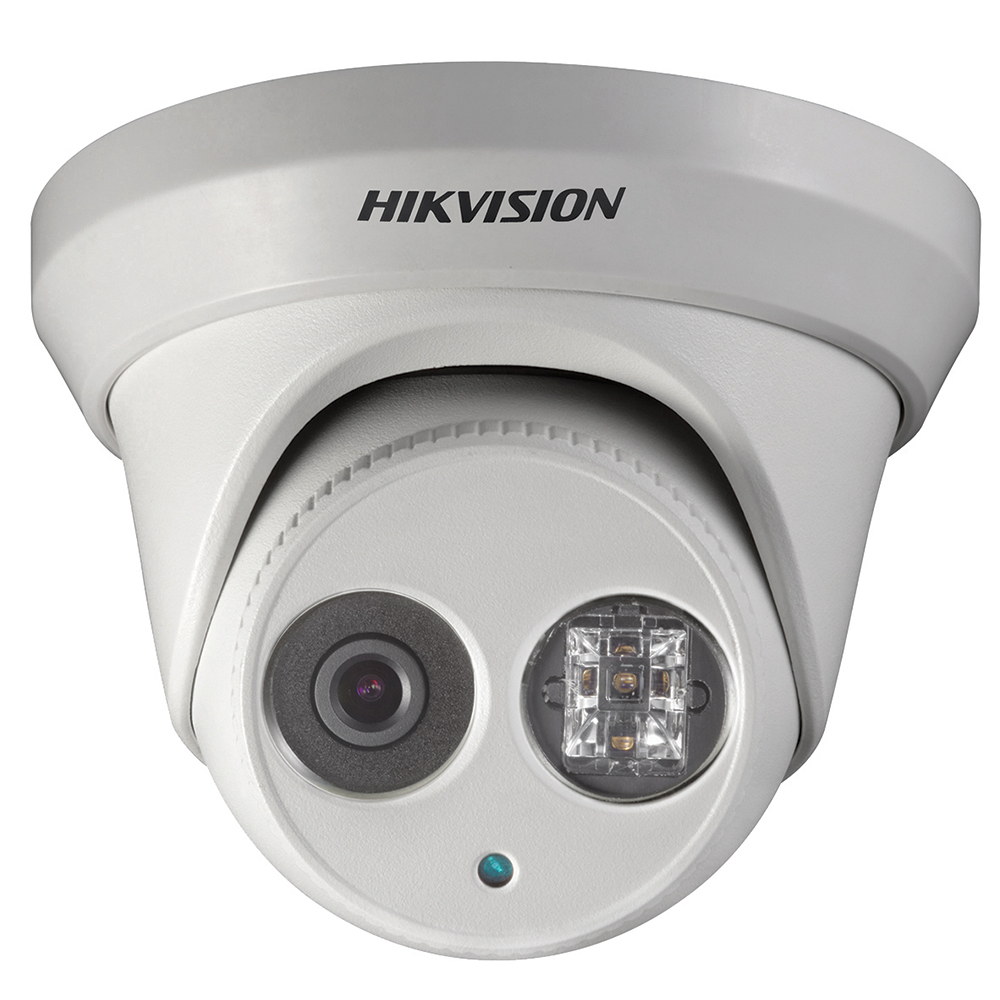

Hikvision 3MP Outdoor Mini Dome, 3D DNR, EXIR IR Tech, 4mm, Fixed Lens, IP66
Read more -

Hikvision 6MP Outdoor Bullet Camera, 25fps, 2.8-12mm Zoom Lens, 50m Smart IR
Read more -

Hikvision DarkFighter, Ultra Low-Light Full Body Camera, 3.8-16mm@F1.5, WDR, ABF, Defog
Read more -

Hikvision NVR, 100Mbps Input , 8 Independent PoE Ports, 2 SATA Interfaces + 3TB HDD
Read more -

Hikvision NVR, 200Mbps Input, 16 PoE Interfaces, 4HDD bays, 1.5U Chassis + 3TB HDD
Read more

